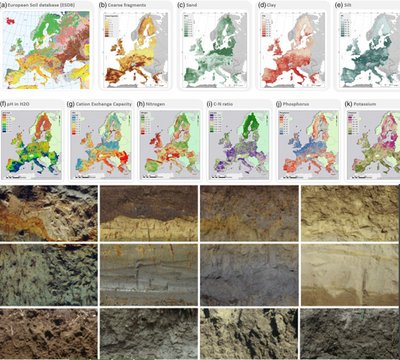
Soil data & Monitoring, mapping and modelling
The amount and specifications of soil data and soil information infrastructures differ across Europe due to differences in needs, methods and knowledge between countries.
Soil profiles, properties, quality, functions & use
Soil information is derived from data on soil profiles, soil properties, soil quality, and data on the functions and use of soils. The processing of data on soil into meaningful information products – such as maps - requires a workflow of collection, organization and management, analysis and publication of soil data.
Harmonized methods and data infrastructures will allow easier sharing of soil data in Europe, which is essential for research and for policy advice on agricultural land.
Modelling and scaling provide insight on how fields, rivers and streets are connected
Water erosion reduces soil quality and causes ecological and economical damages to the environment, to farmers and the society by loss of water storage capacity, organic carbon and essential nutrients, and by their transfer into aquatic environments and urban areas
Modelling and scaling can help us understand how fields, rivers and streets are connected. This insight can help reduce damages from water erosion impacts and provide recommendations for improved mitigation strategies. Strategies for connected landscape elements help reduce water erosion.
Search the Soil data catalogue system
The soil data catalogue is a user friendly search experience.
The catalogue contains:
-
Data products produced in the EJP SOIL and in the wider Soil community
-
An overview of national datasets
Visit the csoil data catalogue via one of the following two points of access:
-
The searchable interface: https://catalogue.ejpsoil.eu
-
A GIT repository GitHub - ejpsoil/ejpsoildatahub (The source of the metadata).
An aspect of the catalogue system is a minimal metadata template in Excel, developed to provide a minimalistic approach to bulk loading records into the catalogue. Alternative available bulk loading initiatives are importing from CSW and DOI (harvesting).
In case you identify potential improvements, create an issue on the git repository or submit an improvement.
Visit the Cookbook on soil data assimilation (wiki)
This cookbook contains recipes on common tasks in soil data assimilation. Soil data assimilation includes metadata management, publication of data, consumption of data and harmonization of data.
Visit the cookbook at https://ejpsoil.github.io/soildata-assimilation-guidance
Mainly developed for technical people working at soil institutes or organizations that need to provide organizational soil data online.
This cookbook has been developed in the scope of the workshops on soil data assimilation provided by WUR & ISRIC in 2022 and 2023.The cookbook is maintained via a participatory versioning system at https://github.com/ejpsoil/soildata-assimilation-guidance.
In case you identify potential improvements, create an issue on the git repository or submit an improvement.
INSPIRE course - April 2022
Guiding national soil information providers towards INSPIRE compliance. What is that? How do you make your data INSPIRE compliant?
EJP SOIL facilitates EU member states to provide Soil data following the INSPIRE Directive with training on: Soil Data good practices
Open Access Materials


Session on the potential implementation of the EU Soil Monitoring Directive proposal in Member States - EJP SOIL Annual Science Days, Vilnius, 2024.
Find the report from the session here.
Contributing projects
Policy briefs

A framework for setting soil health targets and thresholds in agricultural soils
Soil health is defined through soil indicators, which are assessed using targets and/or thresholds. The challenge is that targets and thresholds are highly site-, managementand climate-specific, and there is not yet a validated assessment system with that level of detail.
With policies worldwide being established to promote soil health, there is an urgent need for the development of a system to assess soils.
We explored four approaches to setting targets and thresholds. Based on stakeholder feedback of the approaches, collected in two webinars (EJP SOIL 2023) and case studies of three approaches, we developed a framework that facilitates both choosing the most appropriate target/threshold method for a given context, and using targets and thresholds to promote soil health.
Publications
2023
- Bazzi, H.; Baghdadi, N.; Nino, P.; Napoli, R.; Najem, S.; Zribi, M.; Vaudour, E. Retrieving Soil Moisture from Sentinel-1: Limitations over Certain Crops and Sensitivity to the First Soil Thin Layer. Water 2024, 16, 40.
- Urbina-Salazar, D.; Vaudour, E.; Richer-de-Forges, A.C.; Chen, S.; Martelet, G.; Baghdadi, N.; Arrouays, D. 2023. Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-1 Bare Soil Temporal Mosaics of 6-Year Periods for Soil Organic Carbon Content Mapping in Central France. Remote Sens., 15, 2410.
- Dodin, M., Levavasseur, F., Savoie, A., Martin, L., Foulon, J., & Vaudour, E. (2023). Sentinel-2 satellite images for monitoring cattle slurry and digestate spreading on emerging wheat crop: a field spectroscopy experiment. Geocarto International, 38(1).
- Zayani, H.; Fouad, Y.; Michot, D.; Kassouk, Z.; Baghdadi, N.; Vaudour, E.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Walter, C. 2023. Using Machine-Learning Algorithms to Predict Soil Organic Carbon Content from Combined Remote Sensing Imagery and Laboratory Vis-NIR Spectral Datasets. Remote Sens., 15, 4264.
- Zayani H, Fouad Y, Michot D, Kassouk Z, Lili-Chabaane Z, Walter C. Detecting the temporal trend of cultivated soil organic carbon content using visible near infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy. 2023;31(5):241-255.
- Metzger, K., Liebisch, F.,Herrera, J. M., Guillaume, T., Walder, F., & Bragazza,L. 2023. The use of visible and near- infraredspectroscopy for in- situ characterization ofagricultural soil fertility: A proposition of bestpractice by comparing scanning positions andspectrometers. Soil Use and Management, 40, e12952.
- F. Castaldi, M.H. Koparan, J. Wetterlind, R. Žydelis, I. Vinci, A.Ö. Savaş, C. Kıvrak, T. Tunçay, J. Volungevičius, S. Obber, et al. 2023. Assessing the capability of sentinel-2 time-series to estimate soil organic carbon and clay content at local scale in croplands. ISPRS J. Photogrammetry Remote Sens., 199, pp. 40-60.
- Vasat, R. et al. - 2023. Studying the spatial structure of pedodiversity (Shannon?s entropy) as related to the land area-An example from Czechia
- Nicolas Francos, Daniela Heller-Pearlshtien, José A. M. Demattê, Bas Van Wesemael, Robert Milewski, Sabine Chabrillat, Nikolaos Tziolas, Adrian Sanz Diaz, María Julia Yagüe Ballester, Asa Gholizadeh, Eyal Ben-Dor, - 2023 - "A Spectral Transfer Function to Harmonize Existing Soil Spectral Libraries Generated by Different Protocols", Applied and Environmental Soil Science, vol. 2023, Article ID 4155390, 17 pages, 2023.
2022
- Debaene, G. et al. - 2022. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy for Black Carbon Screening of Agricultural Soils under Industrial Anthropopressure
- Knadel, M. et al. - 2022. Mathematical techniques to remove moisture effects from visible-near-infrared-shortwave-infrared soil spectra-review
- Lopez-Nunes, R. - 2022. Portable X-ray Fluorescence Analysis of Organic Amendments: A Review
- Vandour, E. et al. - 2022. Satellite Imagery to Map Topsoil Organic Carbon Content over Cultivated Areas: An Overview
- Chen, SC. et al. - 2022. Digital mapping of GlobalSoilMap soil properties at a broad scale: A review
- Vanino, S. et al. - 2022. Soil priorities for Italy. A multi-stakeholder consultation, barriers and opportunities for research system
- Boruvka, L. et al. - 2022. Soil priorities for the Czech Republic
- Assennato, F. et al. - 2022. The Impact of Urbanization on Land: A Biophysical-Based Assessment of Ecosystem Services Loss Supported by Remote Sensed Indicators
- Janku, J. et al. - 2022. An overview of a land evaluation in the context of ecosystem services
2021
- Report on harmonized procedures for creation of databases and maps (D6.1)
- Report on the national and EU regulations on agricultural soil data sharing and national monitoring activities (D6.2)
- Proposal of methodological development for the LUCAS programme in accordance with national monitoring programmes (D6.3)
Videos
News articles
RICI - Access to cross-European soil science expertise
‘Resources, Infrastructure and Capabilities Inventory (RICI)’ is an online platform for policy stakeholders. RICI provides access to a pool of specialized scientists and experts at local, regional and national level across Europe. The online inventory is the ‘Yellow pages’ on expertise on soil science in relation to questions for policy matters.